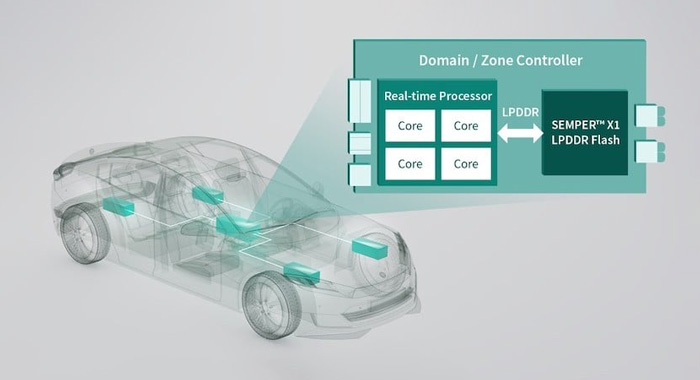
Infineon recently announced that it will launch the industry-first LPDDR flash memory SEMPER X1 to meet the new requirements of the next-generation automotive E/E architecture. The memory chip is being sampled and is expected to be available in 2024.
Compared with NOR, the LPDDR flash memory has higher performance. Through the LPDDR interface, it can provide a throughput of 3.2GB/s, while the random read speed is increased by 20 times, which can realize efficient storage and processing of real-time applications. As a leading German automotive semiconductor company, Infineon memory this time draw on the LPDDR interface solution of the 10-year-old LPDRR4 DRAM, mainly targeting the new requirements of the automotive regional architecture.
Source: Internet
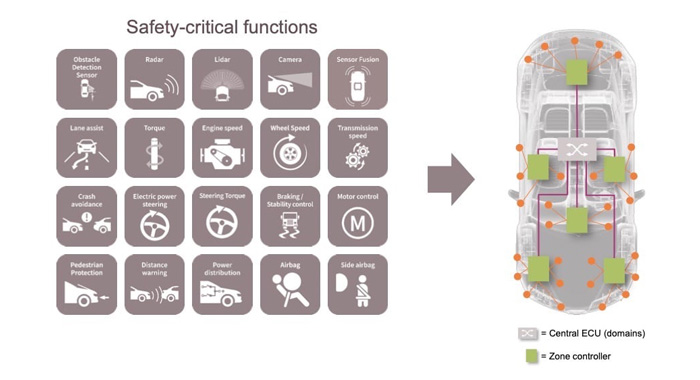
With the development of semi-autonomous vehicles, the automotive storage industry has also experienced structural growth, requiring increased intelligence, connectivity, and complexity of the system. In addition, more and more application scenarios need to be based on high-performance processing units to drive MCU, GPU, MPU, PSoC, and other storage requirements for programs and parameters. The storage requirements of FPGA for structured data are increasing, making The traditional xSPI NOR flash memory can no longer meet the needs of users.
Infineon's LPDDR flash memory can meet the high demand for real-time computing of the regional controller in the car, making the car more reliable and safe, and having higher performance than xSPI NOR flash memory.
Flash Memory
Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It is commonly used in applications such as digital cameras, USB drives, and MP3 players. Flash memory is a form of EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) which is a type of non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed as needed. Flash memory can hold its data even when the power is turned off, unlike RAM (random-access memory) which has to be powered on in order to retain its data. Flash memory is typically smaller, faster, and less expensive than traditional hard drives. It is also more reliable and durable than traditional hard drives as it is not affected by physical shocks or magnetic fields. Flash memory is becoming increasingly popular as it is used in many consumer devices such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and more.
Flash memory comes in several different types, including:
1. NOR Flash: NOR flash is an older type of flash memory that is slower than other types but is used in many embedded applications. It can be programmed and erased in individual bytes, which makes it well-suited for code storage.
2. NAND Flash: NAND Flash is a newer type of flash memory that is faster and cheaper than NOR Flash. It is often used for storing large amounts of data, such as music, photos, and videos.
3. Multi-Level Cell (MLC) Flash: MLC flash is a type of NAND flash that uses multiple levels of storage to store more data in the same space. This type of flash is most commonly found in USB drives.
4. 3D NAND Flash: 3D NAND flash is a newer type of NAND flash that uses layers of memory cells to store more data in the same space. This type of flash is becoming increasingly popular in consumer electronics.
5. eMMC Flash: eMMC flash is a type of flash memory that is used in mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. It is typically used to store the operating system and other apps.
LPDDR Flash Memory
LPDDR (low power double data rate) Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory technology that combines the features of both DRAM and Flash memory. It has the same low power consumption and fast read/write access times of DRAM, but with the added benefit of non-volatility like Flash memory. This makes it an ideal choice for mobile computing devices such as tablets and smartphones, where power consumption and performance are key priorities. LPDDR Flash memory is typically used for the storage of data such as photos, music, and videos. It is also used for applications that require a high level of performance, such as graphics-intensive gaming. The technology is also used in embedded systems, where its high speed and low power consumption make it an ideal choice.
Source: Internet
LPDDR flash memory has several advantages over other types of flash memory. The most significant advantage is its ability to store data with very low power consumption. This is important in portable devices such as smartphones and tablets, where battery life is a major concern. LPDDR flash memory also has a much higher data transfer rate than other types of flash memory, allowing for faster loading times. This is important for applications and other data that need to be accessed quickly.
Another advantage is its ability to store data more reliably than other types of flash memory. This is due to the way it is manufactured. LPDDR flash memory uses a process called Charge Trap Flash (CTF) which prevents data corruption by trapping electrons in a layer of insulation. This makes it less prone to data loss due to power outages or other environmental factors.
Finally, LPDDR flash memory is less expensive than other types of flash memory. This makes it a more affordable option for consumer electronics and other applications that need reliable memory.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the requirements for Flash Memory are becoming increasingly demanding. Flash Memory must be highly reliable and able to withstand the high temperatures and vibrations of automotive environments, as well as have low power consumption. Additionally, Flash Memory must have fast read and write speeds to support the data transfer demands of the automotive industry, be secure enough to protect automotive data from unauthorized access and be cost-efficient in order to be economically viable for automotive applications.
The industry-first automotive LPDDR flash memory from Infineon is an important step in the automotive industry. This new memory technology will enable automotive manufacturers to create powerful, cost-effective solutions for the onboard computing needs of modern cars and trucks. It will also give car manufacturers the flexibility to design and develop systems that are tailored to the specific needs of their vehicles.