MOSFET and IGBT are different transistors for modern electronic and power electronic circuits. Although both are voltage-controlled devices, they perform differently in various aspects. This article provides a basic overview and highlights the main applications of these devices.
The Difference Between MOSFET and IGBT
MOSFET transistors have an insulated gate and use a single layer of metal oxide to control the flow of current, while IGBTs have an insulated gate and a bipolar transistor to control the current. MOSFETs are able to switch at higher frequencies than IGBTs and are usually used in high-speed switching applications. IGBTs require less voltage to turn on and off, making them more efficient than MOSFETs, and are usually used in applications where the switching frequency is not as important. IGBTs also have a higher breakdown voltage than MOSFETs, making them better suited for applications that require high voltage.
MOSFET vs IGBT
What is MOSFET?
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) are three-terminal devices used in many electronic circuits. They are a type of field-effect transistor (FET) that is used to amplify or switch electronic signals. In a MOSFET, the gate terminal controls the flow of electrons between the source and drain terminals. By modulating the voltage applied to the gate terminal, the current between the source and drain terminals can be controlled.
MOSFETs are used extensively in digital and analog switching applications, as well as in many other applications, such as the MOSFET for audio amplifiers, power amplifiers, voltage regulators, and motor controllers. They are also used in many integrated circuits (ICs) and microprocessors.
▪ Enhancement-mode MOSFETs (E-MOSFETs)
▪ Depletion-mode MOSFETs (D-MOSFETs)
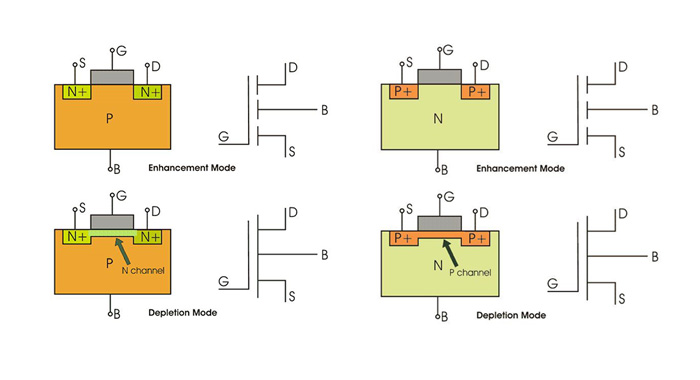
P-Channel Mosfet & N-Channel Mosfet
What is IGBT?
Insulated-gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a type of power semiconductor device used for switching and amplifying electrical signals. It consists of four layers of alternating N-type and P-type material. When a voltage is applied to the gate terminal, it controls the current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals, making it an effective and efficient power switch. In addition, due to its high current and voltage capabilities, the IGBT is often used in power-conversion applications such as inverters, motor drives, voltage regulators, and power supplies. IGBTs are also often used in high-power applications such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, where they provide efficient power conversion and control.

IGBT
IGBT vs MOSFET
IGBT and MOSFET are both usual transistors. Although they can be used interchangeably in certain applications, they differ in construction, operating principles, and performance.
Current and Voltage Capability: MOSFET has advantages in low and medium power applications, the current can reach up to KA, but the withstand voltage capability is relatively weak. IGBT is suitable for high voltage and high current applications and can withstand higher voltage and current. However, the frequency characteristics are not as good as MOSFET.
Switching Speed: With fast switching speed, the operating frequency of MOSFET can reach hundreds of kHz to tens of MHZ. The switching speed of IGBT is slow, the current hard switching speed can reach about 100KHZ.
Loss and Efficiency: In high-frequency applications, the efficiency of MOSFET is higher due to its fast switching speed and low turn-off loss. Although the switching speed of IGBT is slow, it has low loss and high efficiency which is suitable for high-power applications.
Thermal Stability: MOSFET has good thermal stability and is suitable for working in high-temperature environments. IGBT also has high thermal stability, but the specific performance may vary depending on the design and application environment.
Applications of MOSFET and IGBT
Transistors are critical components for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. Although find the usage on the same application fields, MOSFET and IGBT are committed to different aspects.
According the four different features between IGBT and MOSFET, they are applied to different aspects to provide their best performance.
▪ Technology Types
Based on different types of technology, these two devices perform in vary applications. MOSFETs are used in switching applications, while IGBTs are used in high-power applications such as motor control and power conversion.
▪ Switching Speed
MOSFETs are generally able to switch faster than IGBTs, making them better suited for high-frequency applications. IGBTs, however, are better suited for applications that require higher voltage and current ratings.
▪ Power
MOSFETs are better suited for low-power applications, while IGBTs can handle higher power ratings. This makes IGBTs better suited for applications such as motor control and power conversion.
▪ The Types of Devices
The fourth difference is the types of devices they can control. MOSFETs are better suited for switching applications, while IGBTs are better performing in controlling higher-voltage applications such as motor control and power conversion.
Source: Internet
MOSFET Applications
It acted in different roles in various applications. So how MOSFET work in the electronic circuits? For example:
In digital circuits, the MOSFET is used as a switch to control the flow of current. It is used to control the on and off state of transistors, allowing for the construction of logic gates and other digital circuits. It is also used as a voltage regulator, allowing for the precise control of voltage levels in a circuit.
In analog circuits, the MOSFET is used as an amplifier. It is also used to create filters, allowing for the separation of different frequencies from a signal. It is used to create oscillators, allowing for the generation of oscillating electrical signals.
In power electronics, the MOSFET is used as a switch to control the flow of high currents. It is used in motor controllers, power converters, and other applications where high current is needed. It is also used as a voltage regulator, allowing for the precise control of voltage levels.

NTD4963NT4G N-channel MOSFET
For example, the NTD4963NT4G is an N-channel logic level power MOSFET commonly used in power-switching applications. It is particularly well-suited for high current, low voltage DC applications such as automotive and industrial motor controllers, battery management systems, and DC-DC converters. This onsemi MOSFET features a low RDS(ON) of 7.5 mΩ which leads to low power losses, enabling efficient power switching and improved reliability. Additionally, its high-speed switching capabilities combined with low gate charge and low gate-source capacitance allow for faster switching times. This makes the NTD4963NT4G an ideal choice for applications that require high switching frequency and low power losses.
IGBT Applications
Based on their versatility, IGBTs are used in a variety of applications. One of the most common applications is motor control, such as in industrial and automotive applications. IGBTs can be used to control the speed and direction of a motor, as well as the current that is drawn from the power source. This makes them ideal for applications such as variable-speed drives, servo motors, and high-power switching applications.
It also performs in power converters, which are used to convert the electrical energy from one form to another, such as from AC to DC or vice versa. Power converters can be found in a variety of applications, such as in solar power systems, battery charging systems, and uninterruptible power supplies.
In power supplies, they are commonly used in computers and other electronic devices, as they provide a more efficient and cost-effective way of converting electrical energy.
In power-switching applications, it can be used to switch electrical current between two or more circuits. This allows for the efficient and safe distribution of electrical power in a variety of applications, such as in industrial and automotive applications.

IKQ75N120CH3XKSA IGBT of Infineon
For example, the IKQ75N120CH3XKSA is a high-performance insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) module with low power losses and a high operating temperature range. It is widely used in applications that require high switching speeds and low on-state losses, such as motor control, uninterruptible power supplies, solar inverters, and industrial drives. The module also features an advanced current-sharing capability, allowing for multiple IGBTs to be connected in parallel for higher power ratings. Additionally, this Infineon IGBT is designed with a robust heat sink for improved thermal management and greater efficiency.
Conclusion
Overall, MOSFETs are often the preferred choice when it comes to power electronics, due to their lower cost, higher efficiency, and better thermal management. However, IGBTs can be an effective solution in certain applications, such as high-voltage applications. Ultimately, it is important to consider your specific application and choose the best device for the system.